What is RFM Segmentation?
RFM segmentation is a marketing analysis method that involves analyzing customer behavior based on three key factors: recency, frequency, and monetary value. This RFM analysis helps businesses categorize customers into segments, enabling targeted and personalized marketing strategies.
This RFM methodology helps businesses categorize customers into distinct segments, allowing for more effective and targeted marketing strategies tailored to their specific engagement and spending patterns.
This article will provide you with the ins and outs of RFM segmentation – what it means, how to do RFM analysis, and how to perform RFM segmentation effectively.
Guide to Advanced Customer Segmentation
What is RFM in Marketing?
RFM stands for recency, frequency, and monetary. This methodology, known as RFM analysis or RFM customer segmentation, involves evaluating customer behavior based on their transaction recency, frequency, and monetary value. The primary aim is to understand and categorize customers based on their recent purchases, transaction frequency, and overall spending, allowing businesses to implement effective marketing strategies.
What is RFM Analysis?
RFM analysis allows marketers to target specific clusters of customers with communications that are much more relevant for their particular behavior – and thus generate much higher rates of response, plus increased loyalty and customer lifetime value. Like other segmentation methods, an RFM model is a powerful way to identify groups of customers for special treatment..
Marketers typically have extensive data on their existing customers – such as purchase history, browsing history, prior campaign response patterns and demographics – that can be used to identify specific groups of customers that can be addressed with offers very relevant to each.
Why is RFM analysis beneficial?
While there are countless ways to perform segmentation, RFM analysis is popular for three reasons:
- RFM analysis utilizes objective, numerical scales that yield a concise and informative high-level depiction of customers.
- RFM analysisis simple – marketers can use RFM segmentationeffectively without the need for data scientists or sophisticated software.
- RFM analysis is intuitive – the output of this RFM segmentation method is easy to understand and interpret.
Recency, Frequency and Monetary Explained
The three quantifiable factors in the RFM model are recency, frequency and monetary. Below we will explain each factor in detail.
Underlying the RFM segmentation technique is the idea that marketers can gain an extensive understanding of their customers by analyzing these three quantifiable factors::
- Recency: How much time has elapsed since a customer’s last activity or transaction with the brand? Activity is usually a purchase, although variations are sometimes used, e.g., the last visit to a website or use of a mobile app. In most cases, the more recently a customer has interacted or transacted with a brand, the more likely that customer will be responsive to communications from the brand.
- Frequency: How often has a customer transacted or interacted with the brand during a particular period of time? Clearly, customers with frequent activities are more engaged, and probably more loyal, than customers who rarely do so. And one-time-only customers are in a class of their own.
- Monetary: Also referred to as “monetary value,” this factor reflects how much a customer has spent with the brand during a particular period of time. Big spenders should usually be treated differently than customers who spend little. Looking at monetary divided by frequency indicates the average purchase amount – an important secondary factor to consider when segmenting customers.

How to Build an RFM Model: Performing RFM Segmentation & RFM Analysis
The following is a step-by-step, do-it-yourself approach to RFM segmentation. First, we will take a look at RFM Modeling.
What is RFM Modeling?
RFM modeling is a powerful approach to customer segmentation in marketing, standing for recency, frequency, and monetary. This model involves evaluating customer transactions based on how recently they occurred, the frequency of transactions, and their monetary value. Using RFM modeling and RFM segmentation, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer behavior, allowing for more targeted and effective marketing strategies.
Building an RFM model is a structured methodology that starts with the collection and analysis of customer data. This process includes assessing the recency of purchases, the frequency of transactions, and the monetary value associated with each transaction. Once this data is gathered, businesses utilize the RFM methodology to assign numerical scores to each parameter, facilitating the categorization of customers into specific segments. This method is a key aspect of customer segmentation using RFM analysis, providing businesses with a systematic approach to understanding and responding to the diverse needs and behaviors of their customer base.
With the right tools, RFM segmentation can be done automatically, using marketing AI, for more accurate results.
Optimove employs a sophisticated and data-driven approach to RFM segmentation. The platform integrates rich historical, real-time, and predictive customer data to assess three crucial factors: recency, frequency, and monetary value. The system then uses advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence to analyze this data and assign numerical scores to each parameter.
With this numerical representation of customer behavior, Optimove’s RFM segmentation enables businesses to categorize their customer base into distinct segments. These segments help identify and understand different customer profiles, allowing for targeted and personalized marketing strategies. By automating the RFM segmentation process, Optimove ensures that businesses can efficiently leverage this powerful methodology to enhance customer engagement, drive loyalty, and optimize marketing efforts.
Note that with the aid of software, RFM segmentation – as well as other, more sophisticated types of segmentation – can be done automatically, with more accurate results.
Step 1: Assign Recency, Frequency & Monetary Values
The first step in building an RFM model is to assign Recency, Frequency and Monetary values to each customer. The raw data for doing this, which should be readily available in the company’s CRM or transactional databases, can be compiled in an Excel spreadsheet or database:
- Recency is simply the amount of time since the customer’s most recent transaction (most businesses use days, though for others it might make sense to use months, weeks or even hours instead).
- Frequency is the total number of transactions made by the customer (during a defined period).
- Monetary is the total amount that the customer has spent across all transactions (during a defined period).
Step 2: Divide Customers into Tiers
The second step is to divide the customer list into tiered groups for each of the three dimensions (R, F and M), using Excel or another tool. Unless using specialized software, it’s recommended to divide the customers into four tiers for each dimension, such that each customer will be assigned to one tier in each dimension:
| Recency | Frequency | Monetary |
| R-Tier-1 (most recent) | F-Tier-1 (most frequent) | M-Tier-1 (highest spend) |
| R-Tier-2 | F-Tier-2 | M-Tier-2 |
| R-Tier-3 | F-Tier-3 | M-Tier-3 |
| R-Tier-4 (least recent) | F-Tier-4 (only one transaction) | M-Tier-4 (lowest spend) |
This results in 64 distinct customer segments (4x4x4), into which customers will be segmented. Three tiers can also be used (resulting in 27 segments); using more than four, however, is not recommended (because the difficulty in use outweighs the small benefit gain from the extra granularity).
As mentioned above, more sophisticated and less manual approaches – such as k-means cluster analysis – can be performed by software, resulting in groups of customers with more homogeneous characteristics.
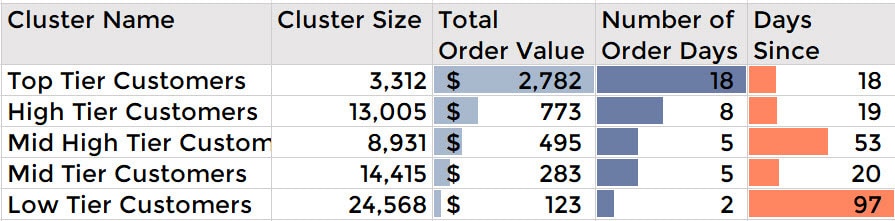
Step 3: Create Customer Groups
The third step is to select groups of customers to whom specific types of communications will be sent, based on the RFM segments in which they appear.
It is helpful to assign names to segments of interest. Here are just a few examples to illustrate:
- Best Customers – This group consists of those customers who are found in R-Tier-1, F-Tier-1 and M-Tier-1, meaning that they transacted recently, do so often and spend more than other customers. A shortened notation for this segment is 1-1-1; we’ll use this notation going forward.
- High-spending New Customers – This group consists of those customers in 1-4-1 and 1-4-2. These are customers who transacted only once, but very recently and they spent a lot.
- Lowest-Spending Active Loyal Customers – This group consists of those customers in segments 1-1-3 and 1-1-4 (they transacted recently and do so often, but spend the least).
- Churned Best Customers – This segment consists of those customers in groups 4-1-1, 4-1-2, 4-2-1 and 4-2-2 (they transacted frequently and spent a lot, but it’s been a long time since they’ve transacted).
Marketers should assemble groups of customers most relevant for their particular business objectives and retention goals.
Step 4: Craft Specific Messaging
The fourth step actually goes beyond the RFM segmentation itself: crafting specific messaging that is tailored for each customer group. By focusing on the behavioral patterns of particular groups, RFM marketing allows marketers to communicate with customers in a much more effective manner.
Again, here are just some examples for illustration, using the groups we named above:
- Best Customers – Communications with this group should make them feel valued and appreciated. These customers likely generate a disproportionately high percentage of overall revenues and thus focusing on keeping them happy should be a top priority. Further analyzing their individual preferences and affinities will provide additional opportunities for even more personalized messaging.
- High-spending New Customers – It is always a good idea to carefully “incubate” all new customers, but because these new customers spent a lot on their first purchase, it’s even more important. Like with the Best Customers group, it’s important to make them feel valued and appreciated – and to give them terrific incentives to continue interacting with the brand.
- Lowest-Spending Active Loyal Customers – These repeat customers are active and loyal, but they are low spenders. Marketers should create campaigns for this group that make them feel valued, and incentivize them to increase their spend levels. As loyal customers, it often also pays to reward them with special offers if they spread the word about the brand to their friends, e.g., via social networks.
- Churned Best Customers – These are valuable customers who stopped transacting a long time ago. While it’s often challenging to re-engage churned customers, the high value of these customers makes it worthwhile trying. Like with the Best Customers group, it’s important to communicate with them on the basis of their specific preferences, as known from earlier transaction data.
Of course, deciding which groups of customers to target and how to best communicate with them is where the art of marketing comes in!
The Guide to Advanced Customer Segmentation
Go in depth on advanced segmentation with this guide which was written based on analyzing tens of thousands of segments across Optimove’s customer base.
Caveats of RFM Segmentation & RFM Model
RFM segmentation is a straightforward and powerful method for customer segmentation. However, the fact that the RFM model only looks at three specific factors (albeit important ones) means that the method may be excluding other variables that are equally, or more, important (e.g., products purchased, prior campaign responses, demographic details).
Also, RFM marketing is, by its nature, an historical method: it looks at past customer behavior that may or may not accurately indicate future activities, preferences and responses. More advanced customer segmentation techniques are based on predictive analytics technologies that tend to be far more accurate at predicting future customer behavior.
Can Machine Learning enhance RFM Segmentation?
RFM segmentation itself is a traditional marketing methodology that does not inherently involve machine learning. It’s a rule-based approach to segmenting customers based on historical data related to their recency, frequency, and monetary behavior.
However, in modern marketing analytics and customer relationship management (CRM), machine learning techniques may be employed to enhance the segmentation process. RFM Machine learning algorithms can analyze more complex patterns and consider a broader range of variables beyond RFM, providing more sophisticated and dynamic customer segmentation.
In summary, while RFM segmentation itself is not a machine learning technique, RFM machine learning can be applied in the broader context of customer segmentation and analysis to uncover more nuanced patterns and insights.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many RFM segments are there?
To determine how many RFM (Recency, Frequency, Monetary) segments there are, you need to divide your customers into tiers within each of the three dimensions (R, F and M).
It’s recommended to create three or four tiers for simplicity when determining the results. With three tiers per dimension, there will be 27 customer segments (3x3x3). When there are four tiers per dimension, there will be 64 customer segments (4x4x4).
What is an ideal RFM score?
An ideal RFM score is the highest score in each of the three dimensions (R, F and M). So, if a business uses a 1 to 5 scale, with 5 being the highest, then the perfect RFM score is 555.
How to do an RFM Analysis?
To conduct an RFM analysis, businesses need to evaluate three key customer metrics: recency, frequency, and monetary value. Assign numerical scores to each metric based on customer behavior, then categorize customers into segments, allowing for targeted marketing strategies.
What is an RFM Model?
An RFM model is a customer segmentation technique that evaluates Recency, Frequency, and Monetary value to categorize customers into segments. For example, in e-commerce, a customer who made a recent purchase, buys frequently, and spends a significant amount would be considered a high-value segment in an RFM model.
Optimove’s RFM software: The Leading Customer Segmentation & CRM Automation Solution
Optimove is a Relationship Marketing Hub that combines the most advanced customer segmentation, modeling and predictive analytics technologies, along with an automated customer marketing orchestration platform that supports both pre-scheduled and realtime campaigns. Optimove’s RFM software is advanced and easy to use. The company’s customer RFM segmentation software helps marketers implement a systematic approach to planning, executing, measuring and optimizing a complete, highly personalized customer marketing plan.
Optimove executes RFM segmentation by leveraging advanced analytics to assess customer behavior based on recency, frequency, and monetary values. The platform employs sophisticated algorithms to analyze transaction data, enabling businesses to categorize customers into distinct segments and tailor marketing strategies to effectively engage each group.
Request a Web demo to learn more about how you can use Optimove to automate a complete system of highly personalized customer marketing activities that increase long-term customer loyalty and lifetime value.
Get a personalized tour of Optimove
Let us show you how to go from tens to hundreds of segments