What is Customer Segmentation?
Customer segmentation is the practice of dividing a company’s customers into groups that reflect similarity among customers in each group. The goal of segmenting customers is to decide how to relate to customers in each segment in order to maximize the value of each customer to the business.
Guide to Advanced Customer Segmentation
What is customer segmentation analysis?
Customer segmentation analysis is the process performed when looking to discover insights that define specific segments of customers. Marketers and brands leverage this process to determine what campaigns, offers, or products to leverage when communicating with specific segments.
For example, a retail brand looking to determine how to reactivate lapsed customers might create a segment of customers who purchased in the past and haven’t purchased or browsed the eCommerce store in the past 30 days. It might then analyze that segment to understand what type of products these customers have purchased in the past, what is their discount affinity and more. Using this information, the marketing team can determine the best campaign to create in order to reactivate these lapsed customers.
Similarly, a company can use customer segmentation analysis to determine the value of certain segments by analyzing a segments predicted Future Value, average order value, loyalty tier distribution, and more.
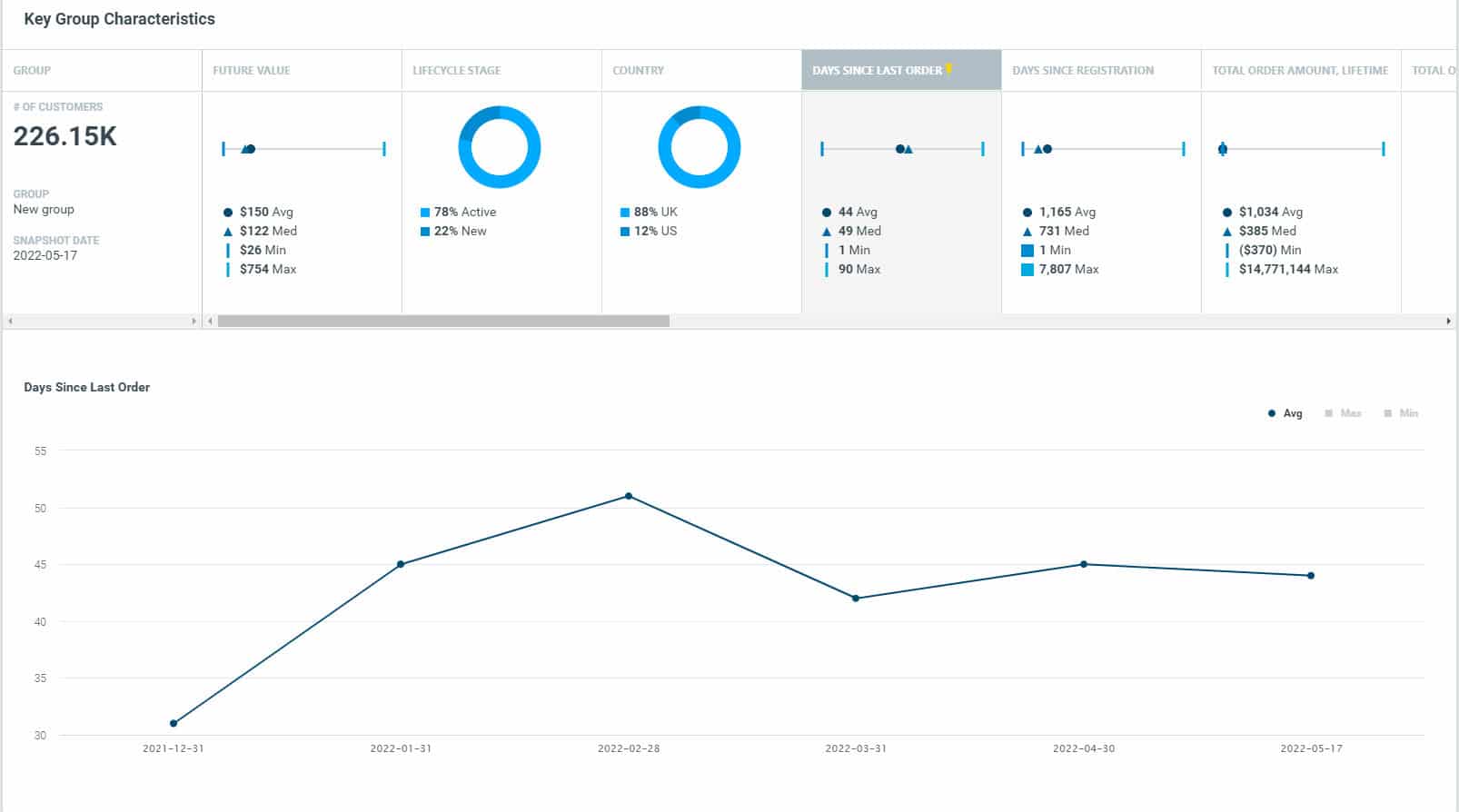
Why is customer segmentation important?
Customer segmentation has the potential to allow marketers to address each customer in the most effective way. Using the large amount of data available on customers (and potential customers), a customer segmentation analysis allows marketers to identify discrete groups of customers with a high degree of accuracy based on demographic, behavioral and other indicators.
Since the marketer’s goal is usually to maximize the value (revenue and/or profit) from each customer, it is critical to know in advance how any particular marketing action will influence the customer. Ideally, such “action-centric” customer segmentation will not focus on the short-term value of a marketing action, but rather the long-term customer lifetime value (CLV) impact that such a marketing action will have. Thus, it is necessary to group, or segment, customers according to their CLV.
CLV-Focused Customer Segmentation
Of course, it is always easier to make assumptions and use “gut feelings” to define rules which will segment customers into logical groupings, e.g., customers who came from a particular source, who live in a particular location or who bought a particular product/service. However, these high-level categorizations will seldom lead to the desired results.
It is obvious that some customers will spend more than others during their relationship with a company. The best customers will spend a lot for many years. Good customers will spend modestly over a long period of time, or will spend a lot over a short period of time. Others won’t spend too much and/or won’t stick around too long.
The right approach to segmentation analysis is to segment customers into groups based on predictions regarding their total future value to the company, with the goal of addressing each group (or individual) in the way most likely to maximize that future, or lifetime, value.

Approaches to Segment Customers
Once you decide the best categories and attributes to base your customer segments on, you must decide what approach you will use to create those segments. The two most common approaches to segmenting customers are rule-based segmentation and cluster-based segmentation.
Rule-based segmentation focuses on setting thresholds to determine what segment a customer should be a part of. The approach segments customers based on a set of rules. The rule-based segmentation approach is a simple way to categorize customers into segments but requires you to determine the attributes used to segment customers each time. It makes it easier to watch trends by looking at how many customers you have in each group. It is difficult to add new attributes, so using the rule-based segmentation approach requires a lot of work to keep segments updated if customers’ behaviors change.
Instead of setting thresholds to divide customers, cluster-based segmentation identifies the best way to segment customers so the segments are as equal as possible. It shows the relationship between data points so they can be put into customer segments. Cluster-based segmentation creates these groups using a K-means algorithm. The cluster-based segmentation approach allows you to find new insights in your data to create segments you did not know existed. It also can put customers into segments using multiple attributes. While cluster-based segmentation provides more segmentation capabilities with little maintenance, it is a difficult approach to set up without a talented data scientist.
Types of Customer Segmentation Models
Accurate customer segmentation involves tracking dynamic changes, and frequently updating new data. Although segmenting customers according to their CLV is the recommended approach, there are many types of customer segmentation models. Some of the more common types are segmentation via cluster analysis, RFM segmentation, and longevity. Some marketers might even combine one or more segmentation models in order to reach their goals.
No matter the types of segmentation models marketers decide to use, they all require marketers to create groupings of customers to serve as a first step in segmenting the customer base. Usually this will result in marketers having a series of tiers for each type of segmentation model. Marketers can then mix different tiers across models to create more defined segments. For example, mixing the highest tier of customers based on an RFM model and combining it with a low longevity tier will result in marketers having a segment of highly active, newly acquired customers.
Customer Segmentation and Machine Learning
An additional approach to customer segmentation is leveraging machine learning algorithms to discover new segments. Different to marketer-designed segmentation models, as the ones described above, machine learning customer segmentation allows advanced algorithms to surface insights and groupings that marketers might find difficulty discovering on their own.
Furthermore, marketers that create a feedback loop between the segmentation model and campaign results will have ever improving customer segments. In these cases, the machine learning model will be not only able to refine its definition of segments, but also be able to identify if a specific subset of the segment is outperforming the rest, optimizing marketing performance.
The Guide to Advanced Customer Segmentation
Go in depth on advanced segmentation with this guide which was written based on analyzing tens of thousands of segments across Optimove’s customer base.
The Optimove Approach to Customer Segmentation
Most frequently, the methods marketers use for segmentation take the form of hard-coded rules based on experience and assumptions. More sophisticated approaches use mathematical models to analyze large amounts of data to group customers with similar data sets into particular segments. However, these approaches ignore a critical component of accurate customer segmentation: how do customers migrate from one segment to another over time?
Optimove uses all available data and employs sophisticated clustering models to perform highly accurate segmentation. In fact, this technology actually results in large numbers of finely sliced micro-segments. However, the “secret sauce” of Optimove’s segmentation is a focus on the dynamic nature of customer behavior. In other words, Optimove continuously recalculates the segmentation of every customer and tracks how customers move from one micro-segment to another over time.
In other words, most companies view segmentation as a method of clustering similar customers together at a given point in time, but they completely disregard the path or route that each customer has taken to reach his or her present segment. By analyzing customers based on their movement among segments over time, Optimove achieves far more accurate segmentation than any other known method.
Furthermore, the combination of this dynamic customer segmentation approach with Optimove’s ability to create extremely homogenous and compact micro-segments results in an unparalleled degree of customer segmentation accuracy. When factoring in Optimove’s core focus on customer lifetime value in all calculations, it is easy to see why Optimove’s ability to predict the response of every customer to any marketing action is a generation ahead of any other marketing action optimization solution.
Customer Segmentation Examples
Musti, a leading Nordic pet care specialist, grew rapidly and the company had to improve its use of customer data to unlock personalized marketing across multiple countries and channels. Using Optimove, it scaled segmentation and brought personalization to a point where 89% of its campaigns targeted less than 0.02% of its customer base.
By applying segmentation, another Optimove client, BetMGM, gains insight into its customers’ behavior that it wouldn’t have otherwise. “We are using Optimove to maximize customer lifetime value in a lot of different ways,” said Claus Hansen, Director of CRM at BetMGM. “That allows us to identify what we need to do with different customer cohorts really early on and understand how to act throughout the different journeys to ultimately maximize the lifetime value.”
We didn’t leave it there and tested it ourselves. We looked at a data set consisting of over 30 million customers and 2,000 campaigns, delivered to target groups ranging in size from one customer per group to groups of over 100,000 customers. For each target group size, we measured the average campaign uplift. The results make it clear that when conducting customer marketing campaigns, segmentation does indeed stand up to its promise. The smaller the target group, the larger the uplift.
It’s important to note that audience segmentation usually falls into two categories: Rule-based and cluster segmentation. Rule-based segmentation is a simple methodology whereby you would identify an attribute you’d want to segment your customers by and set different thresholds to determine what cluster each customer should be a part of. Cluster-based segmentation identifies the optimal way to divide customers to create as homogenous segments as possible within themselves. Many brands use a combination of the two.
And finally, brands using a customer segmentation model find it’s a powerful source when it comes to determining what messaging and strategy you should use when marketing to your customers. Not only is it ideal for sending highly-personalized and relevant messages, but also, it can be used more strategically as it can expose valuable marketing strategies to increase retention and customer lifetime value (CLTV).
To quickly learn how to go from having segments/target groups, to actually personalizing your marketing strategy, you can either watch the short 3-minute video here or read the transcript here.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 5 criteria for choosing a customer segment?
Choosing a customer segment is simple. Here are five criteria for choosing a customer segment that will maximize the value of each individual customer.
- Utilize all available data. Making predictions or assumptions without the use of data will rarely yield results.
- Track dynamic changes. This means frequently updating new data and continuously recalculating the segmentation of every customer. In other words, you want to track as customers move from one micro-segment to another over time.
- Focus on the long term. You want to analyze customer lifetime value. It is critical to avoid focusing on “”action-centric””, short-term customer segmentation, and instead focus on the long-term impact of a marketing action.
- Choose an approach to segmentation. There are two main approaches to customer segmentation: rule-based segmentation and cluster-based segmentation.
- Rule-based segmentation requires you to create a set of rules that represent specific attributes of each customer. This is a simple way to catagorize customers because it divides customers based on just one attribute.
- On the other hand, cluster-based segmentation is used to divide customers into groups based small variations, and with multiple attributes.
- Create micro-segments. Finally, it is important to note that you can create customer segments on a granular level where you are able to create smaller segments from existing segments. This helps deliver hyperpersonalization.
How does Optimove perform customer segmentation?
Optimove uses advanced algorithms developed from the domains of cluster analysis and decision theory. Every piece of available information with potential marketing value is incorporated into the segmentation process, within a hierarchical data structure, including lifecycle stages (e.g., new, active, risk of churn), behavior patterns, previous campaign response history, predicted lifetime value, prediction to churn, demographics and even realtime customer behavior.
Start Using Marketing Action Optimization Today!
Contact us today – or request a Web demo – to learn how you can use Optimove to easily maximize the impact of every marketing action in order to convert more customers, increase the spend of existing customers and reduce customer churn.
Get a personalized tour of Optimove
Let us show you how to go from tens to hundreds of segments